mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A UML class diagram is the preferred way to describe information. | |||
UML class diagram is the preferred way to describe information. | |||
A UML class diagram shows classes and their relations. | A UML class diagram shows classes and their relations. | ||
A Class differs from an Object. The Object is of a Class. The Class may have many instance objects each being of the Class. | A Class differs from an Object. The Object is of a Class. The Class may have many instance objects, each being of the Class. | ||
Class can be regarded as the “Concept” of something. | A Class can be regarded as the “Concept” of something. For example, if I have a class named “Car” – it is likely to symbolize the fact that there are Cars and that Car is a concept that exists, and that there are probably instance objects of this class as my car, your car, and the car with license plate ABC. | ||
[[File:Class car.png|frameless|76x76px]] | [[File:Class car.png|frameless|76x76px]] | ||
A class typically has attributes. One attribute of | A class typically has attributes. One attribute of “Car” might be "License plate number". Attributes must have types. Typical types are [[String]], [[Integer]], [[Double]], and [[DateTime|Datetime]]. | ||
[[File:Class+attributes.png|frameless|155x155px]] | [[File:Class+attributes.png|frameless|155x155px]] | ||
This means that once we have objects of class Car | This means that once we have objects of class "Car", these objects will have a place to store the License plate number of just that car. | ||
Classes typically | Classes typically have relations to other classes (relation, association, and link are sort of synonyms and can be used interchangeably). | ||
[[File:Classes+assosiations.png|frameless|350x350px]] | [[File:Classes+assosiations.png|frameless|350x350px]] | ||
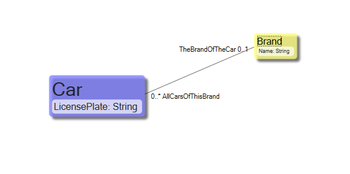
Relations | Relations have two endpoints. The endpoint has a name. When you read a class diagram and your eye follows a relation, you should use the name on the far side of the relation. So in this example, I would say: “There is the concept of <code>Car</code>. <code>Cars</code> has a <code>LicensePlate</code> string. <code>Cars</code> also has a <code>BrandOfTheCar</code> with a <code>Name</code>”. And if I was talking about the brand: “There is the concept of <code>Brand</code>. <code>Brands</code> have a name. <code>Brands</code> also have <code>Cars</code> of the brand that in turn have <code>LicensePlates</code>”. | ||
Relation endpoints also | Relation endpoints also have Cardinality. Cardinality is a rule that describes how many instances there can be in the relation endpoint. The cardinality marking of a star (*) means “unlimited”. Valid cardinality markings are: 0..1 (zero or one instance allowed), 1 (must always have 1 instance), y..x or x where y and x is any number or x is star (*). | ||
These were the basics of UML – there are more, but this is what you need to get started. | |||
* [[Training:UML Inheritance|Read about UML Inheritance]] | |||
* [[Training:Association classes|Read about association classes]] | |||
* [[Training:Composite and Aggregate and what they imply|Read about endpoint aggregation]] | |||
* [[Training:Derived attributes & associations|Read about derived attributes and associations]] | |||
== How Do I Know If It Is Correct? == | |||
The classes we have defined above – along with their attributes and associations – constitute a model. | |||
* A model is always a model of something. | |||
* A model is a simplified version of true/reality concepts that you model. | |||
* The model should have a purpose. | |||
* The validity of the model comes from whether it fulfills its purpose or not. | |||
* There is no universal right or wrong – it all depends on what your needs are. | |||
I could just as well have said that the Brand was an attribute of Car. | |||
== How | |||
The classes we have defined above – along with their attributes and associations – | |||
A model is always a model of something. A model is simplified version of true/reality concepts that you model. The model should have a purpose. The validity of the model comes from | |||
There is no universal right or wrong – it all depends on what your needs are. | |||
I could just as well have said that the Brand was an attribute of Car. | |||
[[File:ClassCar+.png|frameless|224x224px]] | [[File:ClassCar+.png|frameless|224x224px]] | ||
I chose not to since I do not want to have the brand “Plymouth” repeated 10 million times on each and every “Plymouth” (if there are 10 million Plymouth car objects). Instead, I would rather see “Plymouth” typed in once – in the brand class name property (property and attribute are essentially synonyms). This pattern – classifying attributes as concepts on their own – I often refer to as the value store pattern, with the Brand being the ValueStore of brands and each Car instance gets tagged by at most 1 brand. | |||
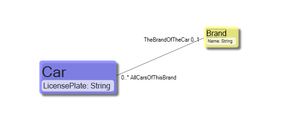
So for me – in this situation – this is better | So for me – in this situation – this is better, but it is not more correct: | ||
[[File:Classes+assosiations.png|frameless|281x281px]] | [[File:Classes+assosiations.png|frameless|281x281px]] | ||
The process of modeling can be | The process of modeling can be visualized as a process of describing important things. As you model, you will have classes that represent physical objects, like Car, but also abstract things like Brand. This is perfectly normal. | ||
This way of describing information does not dictate if you follow the language of the domain you are modeling or not. In principle, you could have named the class Car as “A” and the class Brand as “B”. You could then document someplace else that A is actually Car and B is actually Brand. | |||
You may think that this was a very silly example but this is actually what is done and has been done in thousands of system implementations. Sometimes, it is due to some limitation of the implementation tools and sometimes, it is an ambition to make the resulting system more generic. Think of SAP for example – they call a class “Part” – and document someplace else that for this system instance, "Part" means either a gear or a frame or a saddle. | |||
So if the will to make systems more generic makes your model less readable and more abstract than your reality is, what is the alternative? | |||
The alternative is called Domain Driven Design (or DDD for short) – [https://www.amazon.com/Domain-Driven-Design-Tackling-Complexity-Software/dp/0321125215 this was defined in the book by Eric Evans]. In short, it stipulates you should use the language of the domain you are modeling. This way you – the modeler – and the people working in the domain – get a ubiquitous language and as a result, you understand each other. | |||
My experience is that being as close as possible to the language used by the domain is beneficial to everyone. It makes everything much clearer and easier. Many information architects have done this long before it was given the DDD name. | |||
The MDriven Book - See: [[Training:Association classes|Association classes]] | |||
[[Category:UML]] | [[Category:UML]] | ||
[[Category:The MDriven Book]] | |||
Latest revision as of 05:29, 2 April 2024
A UML class diagram is the preferred way to describe information.
A UML class diagram shows classes and their relations.
A Class differs from an Object. The Object is of a Class. The Class may have many instance objects, each being of the Class.
A Class can be regarded as the “Concept” of something. For example, if I have a class named “Car” – it is likely to symbolize the fact that there are Cars and that Car is a concept that exists, and that there are probably instance objects of this class as my car, your car, and the car with license plate ABC.
A class typically has attributes. One attribute of “Car” might be "License plate number". Attributes must have types. Typical types are String, Integer, Double, and Datetime.
This means that once we have objects of class "Car", these objects will have a place to store the License plate number of just that car.
Classes typically have relations to other classes (relation, association, and link are sort of synonyms and can be used interchangeably).
Relations have two endpoints. The endpoint has a name. When you read a class diagram and your eye follows a relation, you should use the name on the far side of the relation. So in this example, I would say: “There is the concept of Car. Cars has a LicensePlate string. Cars also has a BrandOfTheCar with a Name”. And if I was talking about the brand: “There is the concept of Brand. Brands have a name. Brands also have Cars of the brand that in turn have LicensePlates”.
Relation endpoints also have Cardinality. Cardinality is a rule that describes how many instances there can be in the relation endpoint. The cardinality marking of a star (*) means “unlimited”. Valid cardinality markings are: 0..1 (zero or one instance allowed), 1 (must always have 1 instance), y..x or x where y and x is any number or x is star (*).
These were the basics of UML – there are more, but this is what you need to get started.
- Read about UML Inheritance
- Read about association classes
- Read about endpoint aggregation
- Read about derived attributes and associations
How Do I Know If It Is Correct?
The classes we have defined above – along with their attributes and associations – constitute a model.
- A model is always a model of something.
- A model is a simplified version of true/reality concepts that you model.
- The model should have a purpose.
- The validity of the model comes from whether it fulfills its purpose or not.
- There is no universal right or wrong – it all depends on what your needs are.
I could just as well have said that the Brand was an attribute of Car.
I chose not to since I do not want to have the brand “Plymouth” repeated 10 million times on each and every “Plymouth” (if there are 10 million Plymouth car objects). Instead, I would rather see “Plymouth” typed in once – in the brand class name property (property and attribute are essentially synonyms). This pattern – classifying attributes as concepts on their own – I often refer to as the value store pattern, with the Brand being the ValueStore of brands and each Car instance gets tagged by at most 1 brand.
So for me – in this situation – this is better, but it is not more correct:
The process of modeling can be visualized as a process of describing important things. As you model, you will have classes that represent physical objects, like Car, but also abstract things like Brand. This is perfectly normal.
This way of describing information does not dictate if you follow the language of the domain you are modeling or not. In principle, you could have named the class Car as “A” and the class Brand as “B”. You could then document someplace else that A is actually Car and B is actually Brand.
You may think that this was a very silly example but this is actually what is done and has been done in thousands of system implementations. Sometimes, it is due to some limitation of the implementation tools and sometimes, it is an ambition to make the resulting system more generic. Think of SAP for example – they call a class “Part” – and document someplace else that for this system instance, "Part" means either a gear or a frame or a saddle.
So if the will to make systems more generic makes your model less readable and more abstract than your reality is, what is the alternative?
The alternative is called Domain Driven Design (or DDD for short) – this was defined in the book by Eric Evans. In short, it stipulates you should use the language of the domain you are modeling. This way you – the modeler – and the people working in the domain – get a ubiquitous language and as a result, you understand each other.
My experience is that being as close as possible to the language used by the domain is beneficial to everyone. It makes everything much clearer and easier. Many information architects have done this long before it was given the DDD name.
The MDriven Book - See: Association classes